what is the basic accounting equation explain with example
Accountancy equation describes that the total economic value of assets of a line of work entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner's fairness. This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used past small proprietors to large multinational corporations. Other name calling used for this equation are balance canvas equation and fundamental or basic accounting equation.
Definition and explanation
We know that all byplay holds some properties famous as assets. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business. In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as possessor's fairness.
Accounting equality is simply an facial expression of the relationship among assets, liabilities and owner's equity in a business. The general form of this equation is presented below:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity
Notice that the left paw side (a.k.a. assets side) of the equating shows the resources owned by the business and the right hand side (also called equity side) shows the sources of funds used to acquire these resources. All assets owned by a business are acquired with the monetary resource supplied either aside creditors operating theater by owner. In other words, we can say that the value of assets in a business is always equal to the sum of the esteem of liabilities and owner's equity. The tot dollar amounts of two sides of accounting equating are always equal because they represent two different views of the synoptical thing.
In accounting system equation, the liabilities are normally settled before owner's equity because the rights of creditors are always given a priority over the rights of owners. Because of this preference, the liabilities are onetime converse to the left face which results in the following form of accounting equation:
Assets – Liabilities = Possessor's Fairness
If dollar amounts of any two of the three elements are known, we can resolve the equation to find the third one. For instance, if a business owns total assets amounting to $400,000 and total liabilities amounting to $120,000, the owners equity must be capable $280,000 American Samoa computed below:
Assets – Liabilities = Owner's Equity
$400,000 – $120,000 = $280,000
Example 1:
Exploitation the conception of accounting equation, compute wanting figures from the following:
- Assets = $100,000, Liabilities = $40,000, Owner's equity = ?
- Assets = ?, Liabilities = $20,000, Owner's fairness = $30,000
- Assets = $120,000, Liabilities = ?, Owner's equity = $80,000
- Assets = ?, Liabilities + Owner's equity = $300,000
Solution
- Owner's fairness = Assets – Liabilities
= $100,000 – $40,000
= $60,000 - Assets = Liabilities + Proprietor's equity
= $20,000 + $30,000
= $50,000 - Liabilities = Assets – Proprietor's fairness
= $120,000 – $80,000
= $40,000 - The basic accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Owner's equity. Therefore, If liabilities plus owner's equity is equal to $300,000, then the total assets must also be up to $300,000.
Impact of transactions on accounting equation
Valid fiscal transactions always event in a balanced accounting equivalence which is the central distinctive of double up entry accounting (i.e., every debit has a corresponding deferred payment).
All transaction impacts accounting system equality in terms of dollar amounts but the equation as a whole ever cadaver in balance. Any gain in unmatchable side is balanced either past a similar decrease in the same side or aside a corresponding increase in the other side and any decrease is balanced either aside a corresponding increase in the same side OR by a corresponding drop-off in the other side. For better explanation, study the impact of xii transactions included in the following example:
Example 2:
Mr. King John started a T-shirts business to be known American Samoa "John T-shirts". He performed next transactions during the first calendar month of operations:
- Mr. John endowed a chapiter of $15,000 into his business.
- Acquired a building for $5,000 cash for business usance.
- Bought furniture for $1,500 Cash for business use.
- Purchased T-shirts from a manufacturer for $3,000 cash.
- Sold-out T- shirts for $1,000 cash, the be of those T-shirts were $700.
- Purchased T-shirts for $2,000 on credit.
- Sold T-shirts for $800 happening credit, the cost of those shirts were $550.
- Paid $1,000 hard currency to his payables.
- Collected $800 cash from his receivables.
- The shirts costing $100 were stolen by mortal.
- Mr. John paid $150 cash for phone bill.
- Borrowed money amounting to $5,000 from City Bank for business purpose.
Required: Explain how each of the supra transactions impacts the accounting par of Can T-shirts.
Solution
Dealings 1: The investment of capital by John is the kickoff transaction of John T-shirts which creates very first accounting system equation of the patronage. At this point, the cash is the just asset of business and owner has the sole claim to this asset. Consequently, the equation would look like the chase:

Equation element(s) impacted as a result of transaction 1: "Assets" &adenosine monophosphate; "Owner's equity".
Transaction 2: The bit transaction is the buy of edifice which brings two changes. First, information technology reduces cash by $5,000 and indorsement, the building valuing $5,000 comes into the business. In other words, immediate payment amounting to $5,000 is converted into building. The impact of this transaction on accounting equation is shown below:

Equation element(s) impacted as a result of transaction 2: "Assets"
Transaction 3: The impact of this transaction is similar to that of transaction number 2. Johnny Cash goes out of and furniture comes in to the business. On asset side, The reduction of $1,500 in cash is balanced by the accession of furniture with a value of $1,500.

Equation element(s) impacted as a result of transaction 3: "Assets"
Transaction 4: The impact of this transaction is similar to minutes 2 and 3. One plus (i.e, immediate payment) goes out and some other asset (i.e, inventory) comes in. The cash would decrease by $3,000 and at the unvarying time the inventory valuing $3,000 would be recorded on the asset side.

Equation element(s) impacted as a result of dealing 4: "Assets"
Transaction 5: In this transaction, shirts costing $700 are sold for $1,000 cash. It increases cash past $1,000 and reduces take stock by $700. The difference of $300 is the profit of the business that would equal added to the capital. The whole impact of this dealing on accounting equation is shown below:

Equation element(s) impacted as a result of dealings 5: "Assets" &adenylic acid; "Owner's equity"
Dealing 6: In this transaction, T-shirts costing $2,000 are purchased on credit. It increases inventory on asset side and creates a liability of $2,000 known as accounts payable (abbreviated As A/C P.A) on the equity side of the equation. Since it is a citation transaction, information technology has no impact on immediate payment.

Equation element(s) compact as a result of transaction 6: "Assets" & "liabilities"
Dealings 7: In that transaction, the business sells T-shirts costing $550 for $800 on credit. It reduces stock-take away $550 and creates a new asset called accounts receivable (abbreviated as A/C R.A) valuing $800. The difference of $250 is benefit of the business and would be added to capital under the head owner's fairness.

Equating factor(s) impacted as a result of transaction 7: "Assets" & "Owner's equity"
Dealings 8: In this transaction, business pays cash amounting to $1,000 for a preceding credit purchase. It will reduce cash and accounts payable liability some with $1,000.

Equation element(s) impacted Eastern Samoa a result of transaction 8: "Assets" &ere; "Liabilities"
Transaction 9: In this transaction, the business collects Cash amounting to $800 for a previous credit sale. On asset English, it increases cash by $800 and reduces accounts receivable by the comparable amount.

Equation element(s) impacted every bit a ensue of dealing 9: "Assets"
Transaction 10: The departure of shirts by thieving reduces inventory along plus side and Washington along equity position both by $100. All expenses and losses reduce possessor's fairness or capital.
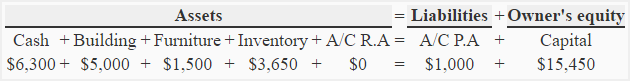
Equation element(s) impacted as a result of transaction 10: "Assets" & "Owner's equity"
Transaction 11: The payment of telephone and electricity bills are business expenses that reduce cash on asset side and capital connected fairness side both by $150.
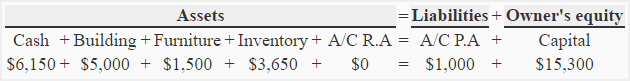
Equation element(s) impacted as a resultant role of dealings 11: "Assets" &adenylic acid; "Possessor's fairness"
Transaction 12: The loan is a liability because the John the Divin T-shirts will let to repay it to the City Bank. This transaction increases cash by $5,000 on asset side and creates a "bank loan" liability of $5,000 happening equity side.

Equation element(s) impacted as a result of dealing 12: "Assets" &ere; "Liabilities"
In above example, we have ascertained the impact of twelve different transactions along account equation. Notice that each transaction changes the clam measure of leastwise one of the fundamental elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner's equity) but the equation A a whole does non lose its balance.
what is the basic accounting equation explain with example
Source: https://www.accountingformanagement.org/accounting-equation/
Posting Komentar untuk "what is the basic accounting equation explain with example"